
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
○ Knee: Extension
Eccentric (Lowering):
○ Knee: Flexion
Form Focus:
Exercise: Leg Extension
Type: Isolation Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Quadriceps (Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralis, Vastus Medialis, Vastus Intermedius)
Secondary Muscles Targeted: None (Pure Isolation Movement)
Equipment: Leg Extension Machine
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions (Lying Leg Curl Machine):
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
○ Knee: Flexion
Eccentric (Lowering):
○ Knee: Extension
Form Focus:

Exercise: Leg Curl
Type: Isolation Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Hamstrings (Biceps Femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus)
Secondary Muscles Targeted: None (Pure Isolation Movement)
Equipment: Leg Curl Machine (Seated, Lying, or Standing)
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
○ Knee: Extension
○ Hip: Extension
Eccentric (Lowering):
○ Knee: Flexion
○ Hip: Flexion
Form Focus:
Exercise: Squats (Barbell)
Type: Compound Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Quadriceps, Gluteus Maximus Secondary Muscles Targeted: Hamstrings, Core, Lower Back, Calves Equipment: Barbell, Squat Rack
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
○ Knee: Extension
○ Hip: Extension
Eccentric (Lowering):
○ Knee: Flexion
○ Hip: Flexion
Form Focus:

Exercise: Lunges (Dumbbells or Barbell)
Type: Compound Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Quadriceps, Gluteus Maximus
Secondary Muscles Targeted: Hamstrings, Calves, Core
Equipment: Dumbbells or Barbell
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
○ Hip: Extension
Eccentric (Lowering):
○ Hip: Flexion
Form Focus:
Exercise: Stiff-Legged Deadlift (Barbell or Dumbbells)
Type: Compound Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Hamstrings, Gluteus Maximus
Secondary Muscles Targeted: Erector Spinae, Core
Equipment: Barbell or Dumbbells
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Pressing Up):
○ Knee: Extension
○ Hip: Extension
Eccentric (Lowering Down):
○ Knee: Flexion
○ Hip: Flexion
Form Focus:
Adjusting your foot placement on the leg press platform can shift muscle activation, allowing you to emphasize different parts of the legs. Here’s how each variation affects muscle recruitment:
○ Shifting your feet higher on the platform increases hip flexion and reduces knee flexion.
○ This variation places greater emphasis on the glutes and hamstrings while reducing quadriceps activation.
○ Glute and hamstring development
○ Reducing stress on the knees
○ A lower foot placement increases knee flexion and reduces hip involvement. ○ This variation places greater stress on the quadriceps.
○ Quadriceps hypertrophy
○ Strengthening the knee joint
○ A wider stance recruits the inner thigh muscles (adductors) more significantly. ○ Also engages the glutes more due to increased hip abduction.
○ Inner thigh development
○ Improved glute activation
○ Enhancing lateral stability
○ A closer stance increases the workload on the vastus lateralis, helping develop outer quad sweep.
○ Also requires greater knee stability and control.
○ Targeting the outer quads for a wider leg appearance
○ Strengthening knee stabilizers
Choosing the Right Foot Placement for Your Goals:
Using a variety of these foot placements in your training can help develop well-rounded leg muscles while reducing overuse injuries.

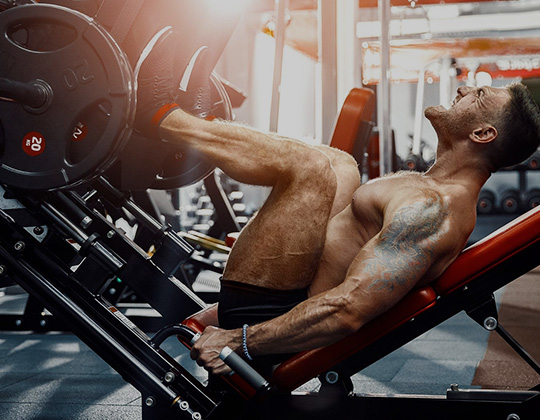
Exercise: Leg Press
Type: Compound Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Quadriceps
Secondary Muscles Targeted: Gluteus Maximus, Hamstrings, Calves
Equipment: Leg Press Machine
Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Instructions:
Key Points & Tips:
○ Toes pointed inward → Targets outer calves
○ Toes pointed outward → Targets inner calves
Benefits:
Muscle Action & Joint Action:
Concentric (Lifting):
Eccentric (Lowering):
Form Focus:
Exercise: Standing Calf Raise
Type: Isolation Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Gastrocnemius (Calves)
Secondary Muscles Targeted: Soleus, Tibialis Anterior (stabilization)
Equipment: Bodyweight, Smith Machine, Dumbbells, or Calf Raise Machine Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles:
Concentric (Pulling Up):
Eccentric (Lowering Down):

Type: Isolation Exercise
Primary Muscles Targeted: Soleus
Secondary Muscles Targeted: Gastrocnemius, Tibialis Anterior (stabilization) Equipment: Seated Calf Raise Machine, Barbell, Dumbbells, or Weight Plates Level: Beginner to Advanced
Muscle Roles: